KNOW HEPATITIS.
BE EMPOWERED.
With knowledge, you will be empowered to take action to take care of yourself and your loved ones. The more information you have, the easier it gets.
The ABCs of Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means “inflammation” of the liver. It is usually caused by infections (bacteria or viruses), medication, alcohol or metabolic disorders (e.g. fatty liver). Viral hepatitis is caused by viruses.
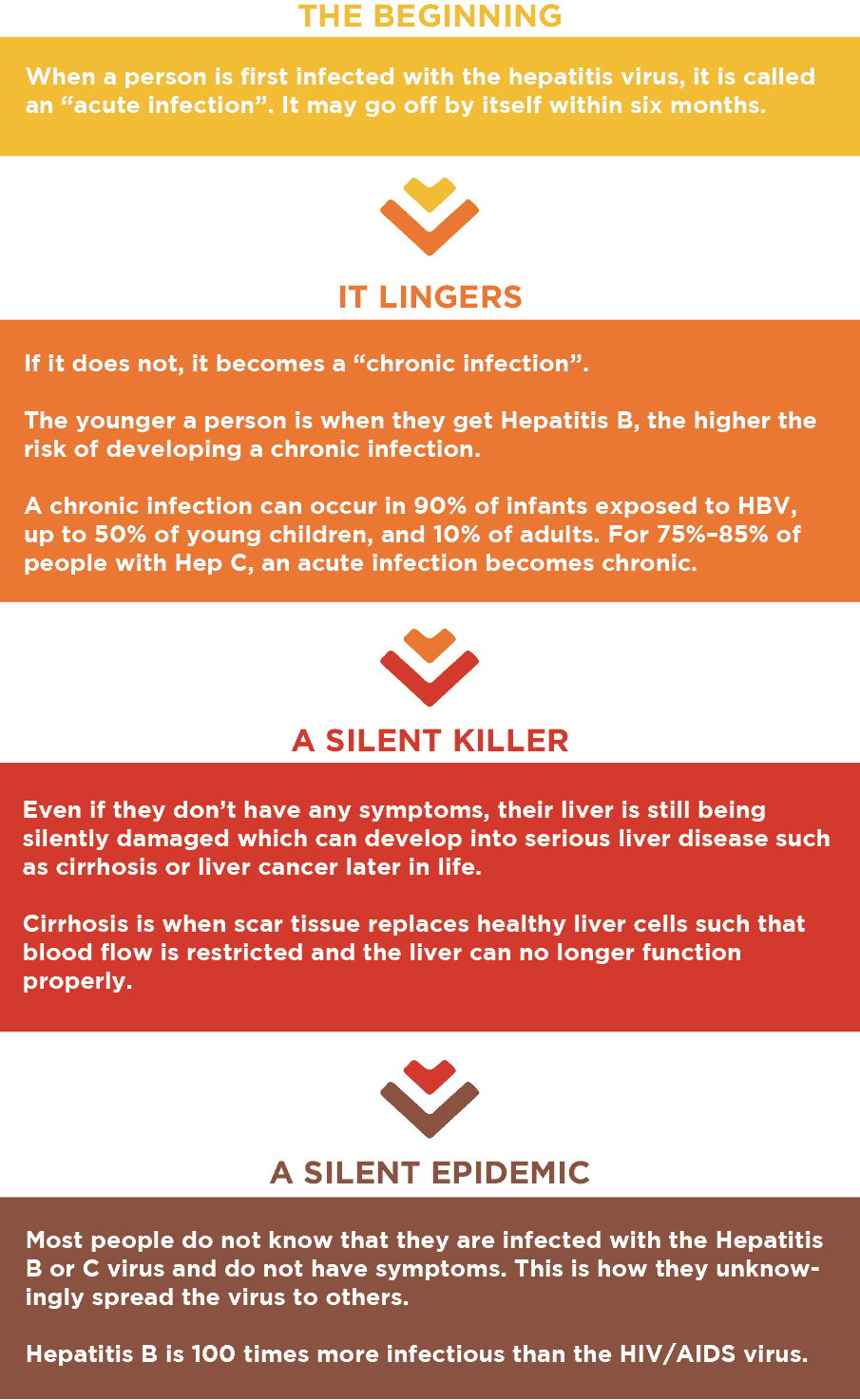
There are currently 5 viruses identified (Hep A, B, C, D and E) that specifically attack the liver and cause “viral hepatitis” or inflammation of the liver due to a virus. All of the hepatitis viruses cause a new or “acute” infection. But only the Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C viruses can result in a “chronic” infection that increases the risk of a person developing cirrhosis, liver failure or liver cancer.

TRANSMISSION
Through contaminated food and water. Thus, can be prevented by good personal hygiene and proper sanitation.
VACCINE
A safe vaccine is available and recommended.
TREATMENT
No drug treatment is needed for a Hep A infection.

TRANSMISSION
Through infected blood, unprotected sex, unsterile or contaminated needles, and from an infected woman to her newborn during childbirth.
VACCINE
There is a vaccine for newborns, children and adults.
TREATMENT
Hep B can be treated but there is no cure.

TRANSMISSION
Through infected blood, unprotected sex, and contaminated or unsterile needles.
VACCINE
There is no vaccine.
TREATMENT
There are now good effective medications for treating Hep C with minimal side effects.

TRANSMISSION
Hep D infection is only possible if a person is already infected with Hep B or a person can be infected with both viruses at the same time.
A Hep D co-infection with Hep B results in more serious and rapid liver damage.
VACCINE
The Hep B vaccine can prevent Hep D

TRANSMISSION
Through contaminated water, food (particularly pork and shellfish), and blood products.
VACCINE
There is no approved vaccine in Singapore, although China has produced and licensed a vaccine.
TREATMENT
Treatment is usually not required. There are unlicensed treatments available should Hep E become chronic, but these instances are rare.
What happens after I am infected?
The Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C viruses can be transmitted by small amounts of blood and can live outside the body for up to several weeks. They can get into the body through minor wounds or cuts that you may not even notice.

How will I know I am infected with the Hep B or Hep C virus?
Most people do not know. Most people do not have symptoms.
Even with symptoms, many people think they have the flu and unknowingly pass the virus to others.
Testing is the only way to know for sure if you are infected.
Common Symptoms
of Hep B and Hep C infection

Fever, fatigue, muscle or joint pain

Loss of appetite

Mild nausea and vomiting

Stomach pain
Serious Symptoms
that require immediate medical attention
Yellow eyes and skin (called "jaundice")

Dark, tea colored urine

Bloated or swollen stomach
Hep B can be treated. Hep C can be cured.
A Hep B or Hep C infection is NOT A DEATH SENTENCE if detected early and treated.




